What is Ability to Benefit?
The Ability to Benefit (ATB) provision in the Higher Education Act gives adults without a high school diploma or equivalent access to federal student aid. ATB is a critical dual enrollment strategy for ensuring equitable access to postsecondary education for adults working to complete their secondary credential. Unfortunately, ATB is poorly understood and massively underutilized, in no small part due to the fluctuation of legislative approval.
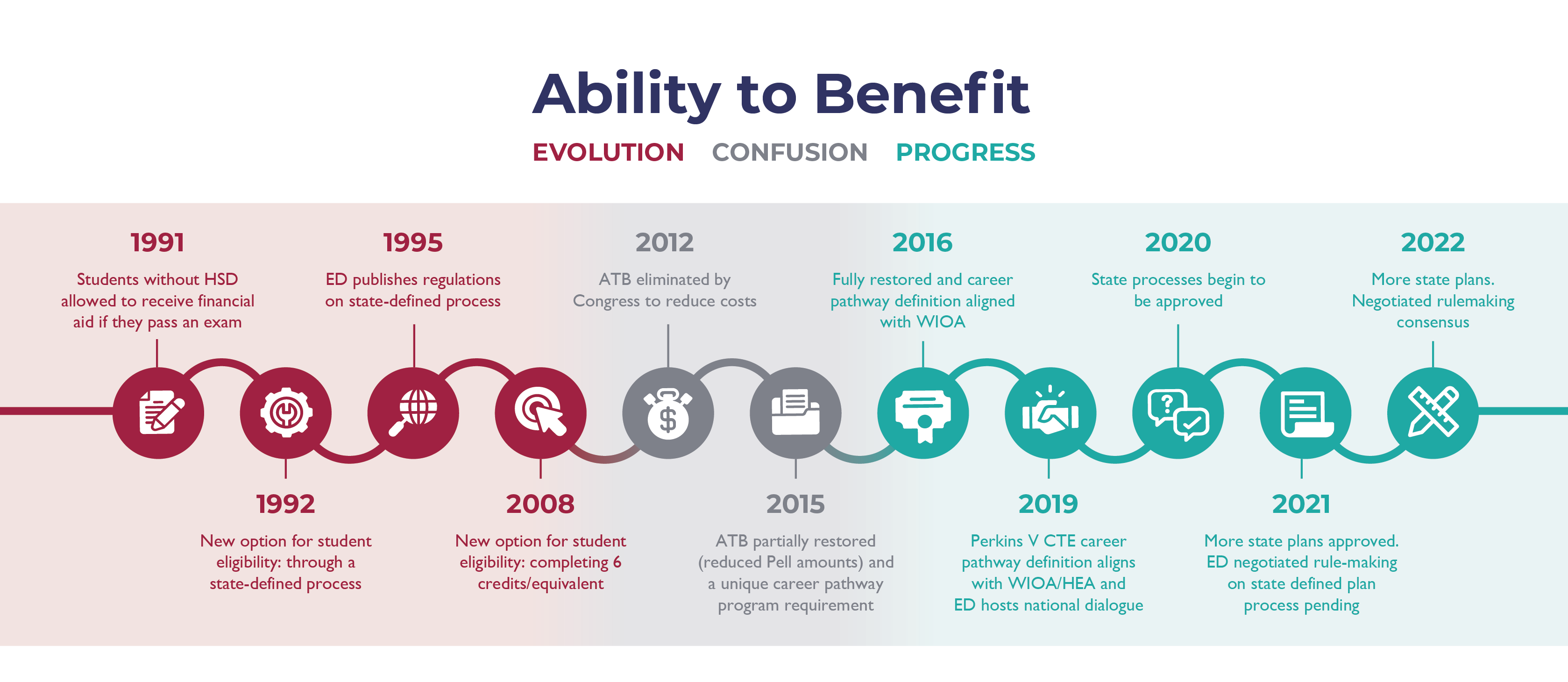
Under ATB, eligible adults can receive federal student aid (primarily Pell Grants) to simultaneously complete their high school credential while earning a postsecondary credential. To be eligible for ATB, an adult must enroll in an eligible career pathway program AND do one of three options:
- pass a US Department of Education-approved test;
- complete 6 credit hours towards a postsecondary credential; or
- be admitted through a “state defined process.”
Learn more about Ability to Benefit.
NCTN’s ATB Projects
NCTN provides technical assistance to state systems to scale and sustain Ability to Benefit implementation. If you are seeking technical assistance for your state or institution, email Sandy Goodman at sandy_goodman@worlded.org.
- A2B4Equity (2022-2024)
- Adult Dual Enrollment through Ability to Benefit (2019-2020)
- Advancing ATB for Equitable Access to Opportunity (2022-2023)
- Communities for Advancing ATB (2024-2025)
ATB Resources
NCTN has compiled a comprehensive list of ATB resources for states and practitioners. View the ATB resources page.
NCTN Resources on ATB
- Resource: Ability to Benefit Eligible Career Pathway Program Documentation Template (2024): Starting on January 1, 2025, all institutions using Ability to Benefit (ATB) will need to upload documentation using the Electronic Eligibility Application (E-App) to demonstrate that one of its ATB Career Pathway Programs meets the eligibility requirements. This template is intended to support ATB-using institutions in identifying the documentation needed to meet these new requirements.
- Blog series: The Ability to Benefit Provision: Expanding Access to College for Adult Learners (2023): A five-part blog series making the case for Ability to Benefit and highlighting the work of three states and further opportunities for investment.
- The Case for Ability to Benefit (11/1/23)
- Case Study: Ability to Benefit in California (11/8/23)
- Case Study: Ability to Benefit in North Carolina (11/15/23)
- Case Study: Ability to Benefit in Texas (11/22/23)
- Opportunities for Further Investment in Ability to Benefit (11/29/23)
- Blog post: New Rules Coming for Ability to Benefit (2022): Details on upcoming changes for Ability to Benefit as a result of the U.S. Department of Education negotiated rulemaking in 2021-2022.
- Webinar: Ability to Benefit State Leadership (2020): Learn about three different strategies that state agencies are using to expand Ability to Benefit and make it easier for adults to simultaneously earn their high school and college credentials.